Comprendre le Diabete de Type 2 : Un Guide Complet
Dec 05, 2024
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Unlike type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin at all, type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. When the body can’t use insulin effectively, blood sugar levels rise, which can lead to serious health problems if left uncontrolled.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to the development of the disease. These include:
- Genetics: Family history can increase the risk.
- Lifestyle Choices: Being overweight or obese, especially with excess body fat around the abdomen, increases insulin resistance.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to the development of diabetes.
- Diet: A poor diet, particularly one high in processed foods and low in fiber, increases the risk.
- Age: The risk increases as people get older, particularly after the age of 45.
- Other Health Conditions: High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) also increase the risk.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
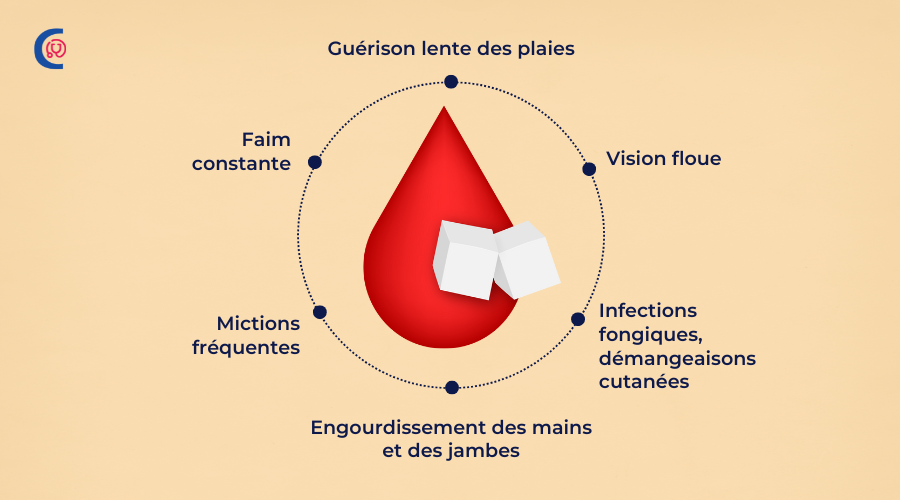
Type 2 diabetes often develops slowly, and many people may not experience noticeable symptoms in the early stages. When symptoms do appear, they can include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of cuts or infections
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
These symptoms occur because of high blood sugar levels and the body's inability to effectively utilize glucose. It’s important to note that type 2 diabetes can go unnoticed for years, which is why regular health check-ups are crucial for early detection.
Diagnosis and Blood Sugar Levels
To diagnose type 2 diabetes, doctors will typically perform blood tests to measure glucose levels. The most common tests include:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood sugar after an overnight fast.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Measures blood sugar after fasting and drinking a sugary solution.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test: Provides an average of a person’s blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
If blood sugar levels are consistently above normal ranges, a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is made.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Managing type 2 diabetes requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and, in some cases, insulin therapy. Here’s how it can be managed:
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fiber, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential. Limiting sugar and processed foods is also important.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps control blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity most days of the week.
2. Medications
- Oral Medications: Medications such as metformin help the body use insulin more effectively.
- Injectable Medications: In some cases, insulin or other injectable medications may be necessary if oral medications don’t work.
3. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar is important to ensure it stays within the target range and prevent complications.
Complications of Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes
If type 2 diabetes is not managed properly, it can lead to serious long-term health complications. These include:
- Heart Disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Kidney Damage: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Vision Problems: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blindness.
- Nerve Damage: Diabetes can cause peripheral neuropathy, leading to tingling, numbness, and even amputations.
- Slow Healing and Infections: Diabetes impairs the body’s ability to fight infections and heal wounds.
The longer someone has diabetes without proper management, the greater the risk of developing these complications.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
While type 2 diabetes can sometimes be genetic, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease. Preventive measures include:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Keeping weight within a healthy range helps reduce insulin resistance.
- Staying Active: Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity.
- Eating a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps manage blood sugar levels.
- Not Smoking: Smoking can worsen the complications of diabetes and increase the risk of developing the disease.
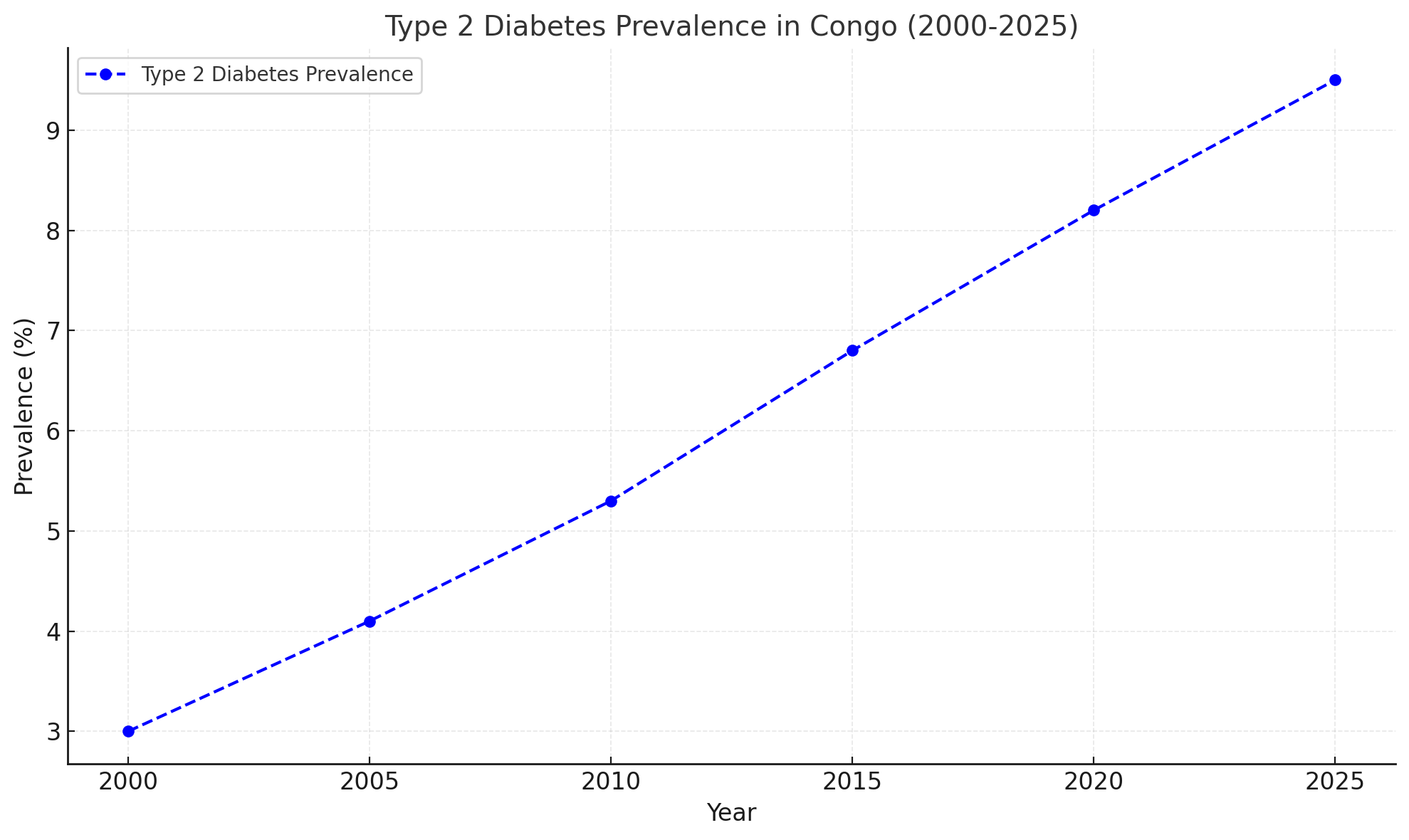
Le graphique montre une augmentation constante de la prévalence du diabète de type 2 parmi la population adulte du Congo de 2000 à 2025. De 3,0 % en 2000, la prévalence s'élève à environ 9,5 % d'ici 2025. Cette tendance à la hausse est probablement influencée par l'urbanisation. , un changement d'habitudes alimentaires et une activité physique réduite. Étant donné que les facteurs liés au mode de vie jouent un rôle important dans le développement du diabète de type 2, l'augmentation de la prévalence souligne la nécessité d'initiatives de santé ciblées, notamment une éducation sur une bonne nutrition, une activité physique régulière et un diagnostic précoce pour aider à prévenir et à gérer efficacement la maladie.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is a manageable condition with the right approach to treatment and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and consistent management of blood sugar levels are essential to preventing complications and improving quality of life. By making small, sustainable changes to diet and physical activity, individuals with type 2 diabetes can lead healthy lives and reduce the risk of long-term health issues. Regular medical check-ups and working closely with a healthcare team are key to managing the condition effectively and ensuring better health outcomes.
Recent Post
Consultations Medicales Gratuites en RDC – CongoRx Soutient les Victimes du Conflit

Dystrophie Musculaire : Causes, Symptomes et Traitements

Guide Complet sur la Meningite : Diagnostic et Soins en Ligne

Comprendre les Cephalees en Grappe : Causes, Symptomes et Traitements | CongoRx
Infections des Voies Urinaires (IVU) : Causes, Symptomes, Prevention et Traitement | CongoRx
Virus HMPV : Symptomes, Transmission et Traitement du Virus Respiratoire

Comprendre le Cycle Menstruel : Guide Complet pour la Sante Feminine

Dengue : Symptomes, Causes et Consultation en Ligne au Congo

Soins de la thyroide : traitements et precautions en ligne
Thyroede : Symptomes, Mesures de Securite et Prevention



